Technology
The Future of Crypto Payments in the Retail Market
In the original whitepaper, Satoshi Nakamoto envisioned Bitcoin as a peer-to-peer version of electronic cash that would facilitate transactions without the oversight on a trustworthy, centralized party.
Since then, cryptocurrency has surged in popularity as an asset class – and Bitcoin is now just one of many digital currencies out there. Investment has poured into the sector because many see the blockchain as an important foundational technology for the future, and it’s also gained traction for speculative reasons.
However, strictly from a payments perspective, certain issues have cropped up since the original Bitcoin vision was outlined, and they’ve ultimately prevented crypto from receiving mainstream adoption as a currency for day-to-day transactions.
What are these obstacles, and how will they be overcome?
The Retail Opportunity
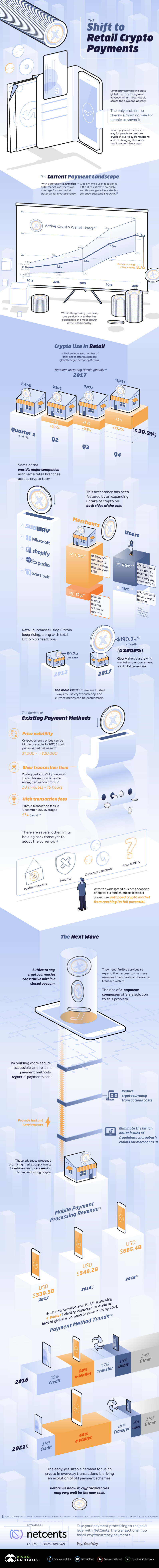
Today’s infographic comes to us from NetCents, and it highlights the growing acceptance of cryptocurrency by retailers and a willingness for consumers to consider using it.
Importantly, the graphic also highlights the major hindrances preventing crypto from reaching mass payment adoption, as well as how the future may look significantly different than today.
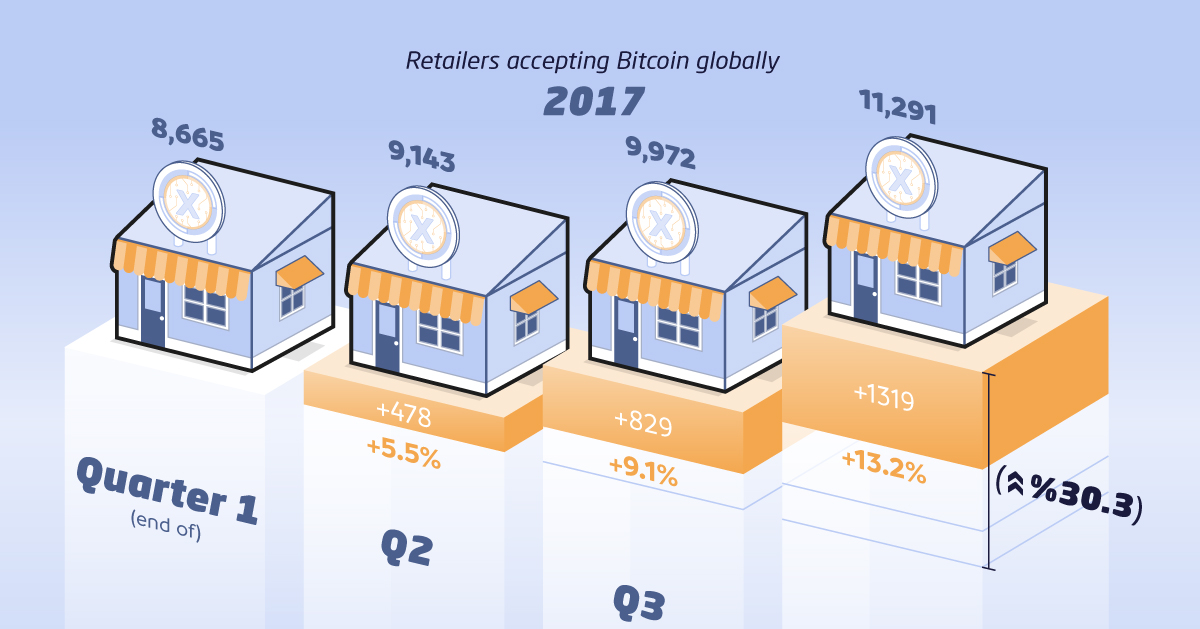
In 2017, the amount of brick-and-mortar retailers accepting crypto grew by 30.3% to 11,291 retailers globally.
At the same time, users have also warmed up to the idea: a recent survey found that 40% of people familiar with the digital currency would be open to using it in everyday transactions.
So why aren’t most people able to buy a coffee at their neighborhood cafe with Bitcoin?
Payment Challenges
There are three main obstacles to using cryptocurrency for everyday transactions. (Note: this list mainly focuses on Bitcoin examples)
1. Price volatility
In 2017 alone, the Bitcoin price fluctuated between $1,000 and $20,000. Big swings in price make it unattractive for day-to-day transactions.
2. Slow transaction times
The average confirmation for Bitcoin takes about 20 minutes per transaction right now – but during past stretches of activity (such as in Jan 2018), it got as high as 41 hours.
3. High transaction fees
The average transaction costs around $1 right now, but just months ago, the average Bitcoin transaction costed $40.
These factors are not necessarily problematic at all times – but one can see why these challenges may make crypto less appealing for everyday retail transactions, such as one at the grocery store or the local coffee shop.
Crypto to the Masses?
Despite these concerns, there is much optimism that crypto can be a boon to retailers – even brick-and-mortar ones. The blockchain is still new, and people around the world are working to solve these payments issues night and day.
Crypto e-payments companies are constantly introducing new technologies and features that could potentially decrease transaction costs and provide instant settlements for retailers, while also eliminating the issue of fraudulent chargebacks. Making ground on these issues would make crypto significantly more appealing to the masses as a form of payment.
What else needs to be done to push crypto into the mainstream?
Technology
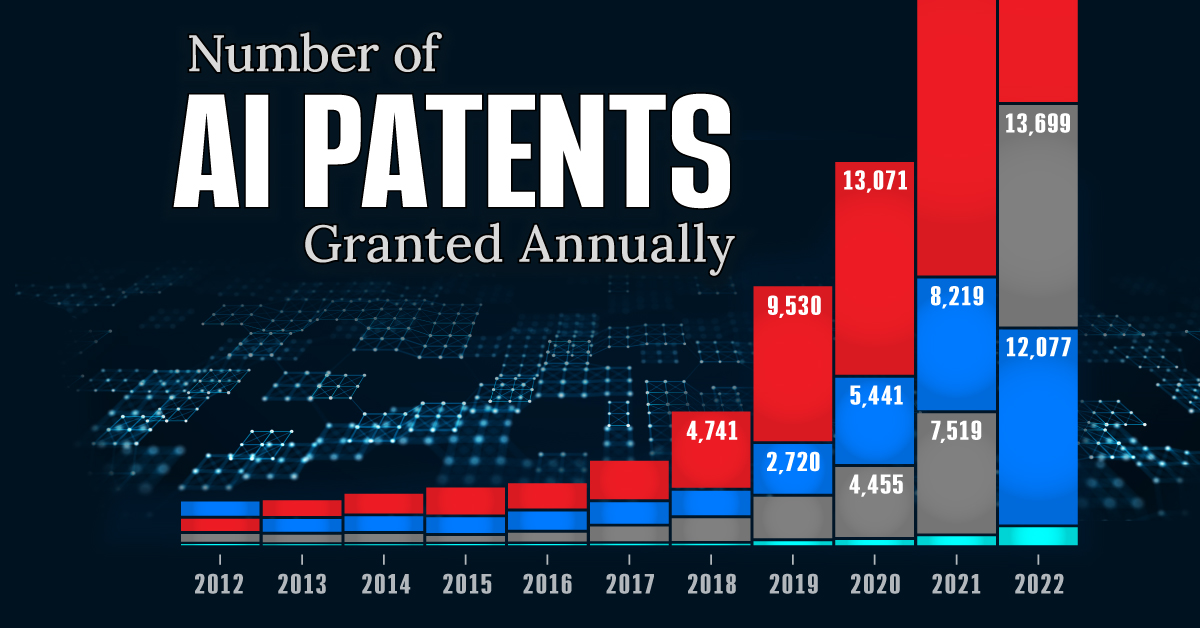
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
Visualizing AI Patents by Country
This was originally posted on our Voronoi app. Download the app for free on iOS or Android and discover incredible data-driven charts from a variety of trusted sources.
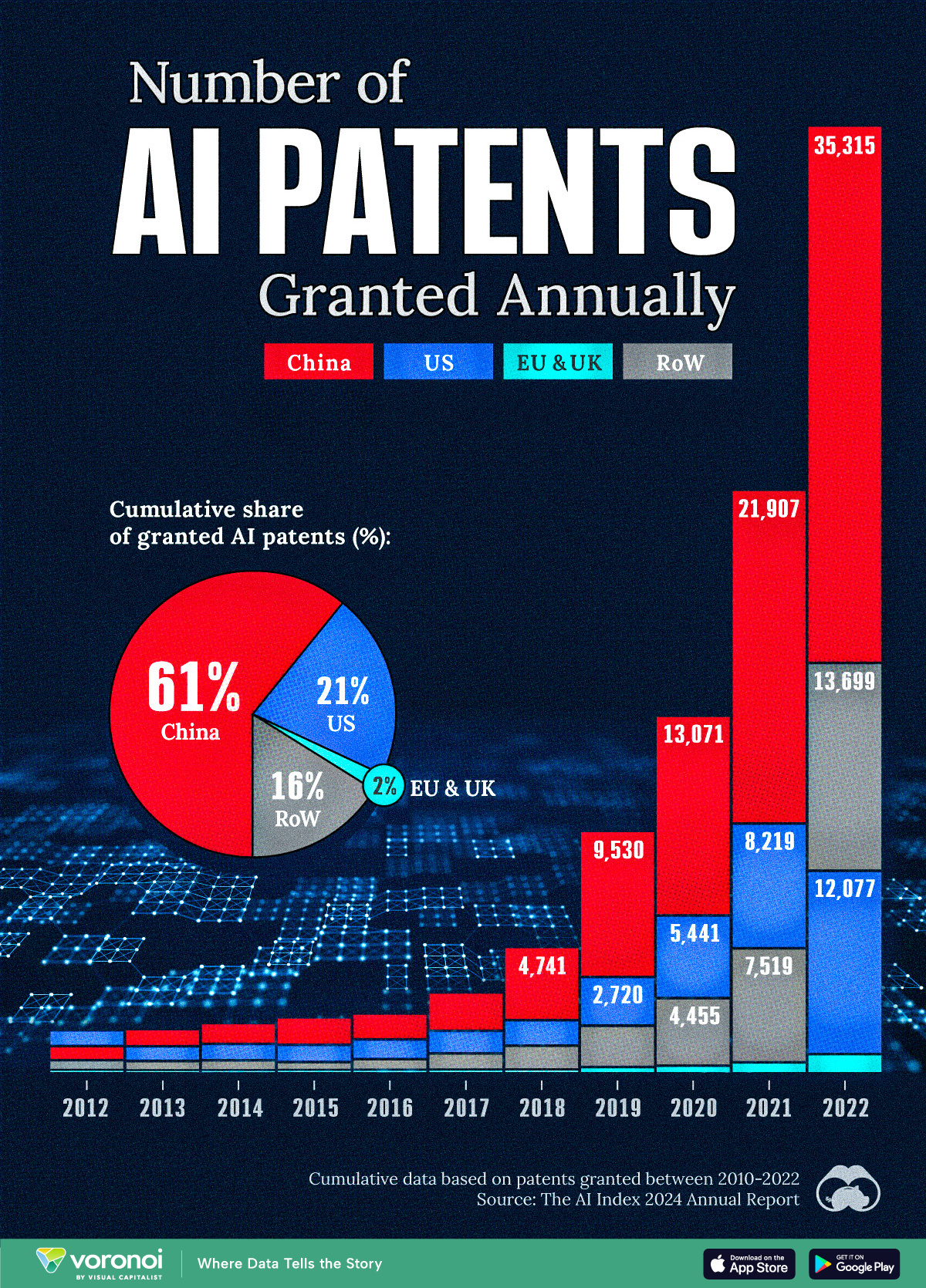
This infographic shows the number of AI-related patents granted each year from 2010 to 2022 (latest data available). These figures come from the Center for Security and Emerging Technology (CSET), accessed via Stanford University’s 2024 AI Index Report.
From this data, we can see that China first overtook the U.S. in 2013. Since then, the country has seen enormous growth in the number of AI patents granted each year.
| Year | China | EU and UK | U.S. | RoW | Global Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 307 | 137 | 984 | 571 | 1,999 |
| 2011 | 516 | 129 | 980 | 581 | 2,206 |
| 2012 | 926 | 112 | 950 | 660 | 2,648 |
| 2013 | 1,035 | 91 | 970 | 627 | 2,723 |
| 2014 | 1,278 | 97 | 1,078 | 667 | 3,120 |
| 2015 | 1,721 | 110 | 1,135 | 539 | 3,505 |
| 2016 | 1,621 | 128 | 1,298 | 714 | 3,761 |
| 2017 | 2,428 | 144 | 1,489 | 1,075 | 5,136 |
| 2018 | 4,741 | 155 | 1,674 | 1,574 | 8,144 |
| 2019 | 9,530 | 322 | 3,211 | 2,720 | 15,783 |
| 2020 | 13,071 | 406 | 5,441 | 4,455 | 23,373 |
| 2021 | 21,907 | 623 | 8,219 | 7,519 | 38,268 |
| 2022 | 35,315 | 1,173 | 12,077 | 13,699 | 62,264 |
In 2022, China was granted more patents than every other country combined.
While this suggests that the country is very active in researching the field of artificial intelligence, it doesn’t necessarily mean that China is the farthest in terms of capability.
Key Facts About AI Patents
According to CSET, AI patents relate to mathematical relationships and algorithms, which are considered abstract ideas under patent law. They can also have different meaning, depending on where they are filed.
In the U.S., AI patenting is concentrated amongst large companies including IBM, Microsoft, and Google. On the other hand, AI patenting in China is more distributed across government organizations, universities, and tech firms (e.g. Tencent).
In terms of focus area, China’s patents are typically related to computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers and systems to interpret visual data and inputs. Meanwhile America’s efforts are more evenly distributed across research fields.
Learn More About AI From Visual Capitalist
If you want to see more data visualizations on artificial intelligence, check out this graphic that shows which job departments will be impacted by AI the most.
-

 Markets1 week ago
Markets1 week agoU.S. Debt Interest Payments Reach $1 Trillion
-

 Business2 weeks ago
Business2 weeks agoCharted: Big Four Market Share by S&P 500 Audits
-

 Real Estate2 weeks ago
Real Estate2 weeks agoRanked: The Most Valuable Housing Markets in America
-

 Money2 weeks ago
Money2 weeks agoWhich States Have the Highest Minimum Wage in America?
-

 AI2 weeks ago
AI2 weeks agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoRanked: The World’s Top Flight Routes, by Revenue
-

 Demographics2 weeks ago
Demographics2 weeks agoPopulation Projections: The World’s 6 Largest Countries in 2075
-

 Markets2 weeks ago
Markets2 weeks agoThe Top 10 States by Real GDP Growth in 2023