hepatic duct
Also found in: Dictionary, Thesaurus, Encyclopedia, Wikipedia.
duct
[dukt]a passage with well-defined walls, especially a tubular structure for the passage of excretions or secretions. adj., adj ductal.
accessory duct of Santorini a tubular structure that drains the lower part of the head of the pancreas.
alveolar d's small passages connecting the respiratory bronchioles and the alveolar sacs.
Bartholin's duct (duct of Bartholin) the larger and longer of the sublingual ducts.
bile d's (biliary d's) see bile ducts.
cochlear duct a spiral membranous tube in the bony canal of the cochlea between Reissner's membrane and the basilar membrane; it is divided into the scala tympani, scala vestibuli, and spiral lamina. Called also scala media.
common bile duct a duct formed by the union of the cystic and hepatic ducts; see also bile ducts.
cystic duct the passage connecting the gallbladder neck and the common bile duct.
efferent duct any duct that gives outlet to a glandular secretion.
ejaculatory duct the duct formed by union of the ductus deferens and the duct of the seminal vesicles, opening into the prostatic urethra on the colliculus seminalis.
endolymphatic duct a canal connecting the membranous labyrinth of the ear with the endolymphatic sac.
excretory duct one through which the secretion is conveyed from a gland.
hepatic duct the excretory duct of the liver, or one of its branches in the lobes of the liver; see also bile ducts.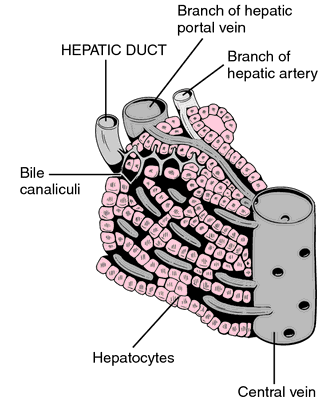

Hepatic duct. From Applegate, 2000.
lacrimal duct the excretory duct of the lacrimal gland; see also lacrimal apparatus. Called also lacrimal canaliculus.
lacrimonasal duct nasal duct.
lactiferous d's ducts conveying the milk secreted by the lobes of the breast to and through the nipples.
lymphatic duct, left thoracic duct.
lymphatic d's see lymphatic ducts.
mammary duct lactiferous ducts.
mesonephric duct an embryonic duct of the mesonephros, which in the male becomes the epididymis, ductus deferens and its ampulla, seminal vesicles, and ejaculatory duct, and in the female is largely obliterated.
müllerian duct either of the two paired embryonic ducts developing into the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes, and becoming largely obliterated in the male.
nasal duct (nasolacrimal duct) the downward continuation of the lacrimal sac, opening on the lateral wall of the inferior meatus of the nose; see also lacrimal apparatus.
pancreatic duct the main excretory duct of the pancreas, which usually unites with the common bile duct before entering the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla; see also bile ducts.
papillary d's straight excretory or collecting portions of the renal tubules, which descend through the renal medulla to a renal papilla.
paramesonephric duct müllerian duct.
paraurethral d's Skene's glands.
parotid duct the duct by which the parotid glands empty into the mouth.
prostatic d's minute ducts from the prostate, opening into or near the prostatic sinuses on the posterior wall of the urethra.
lymphatic duct, right a vessel draining lymph from the upper right side of the body, receiving lymph from the right subclavian, jugular, and mediastinal trunks when those vessels do not open independently into the right brachiocephalic vein.
salivary d's the ducts of the salivary glands.
semicircular d's the long ducts of the membranous labyrinth of the ear.
seminal d's the passages for conveyance of spermatozoa and semen.
sublingual d's the excretory ducts of the sublingual salivary glands.
submandibular duct (submaxillary duct) the duct that drains the submandibular gland and opens at the sublingual caruncle.
tear duct lacrimal duct.
thoracic duct a duct beginning in the cisterna chyli and emptying into the venous system at the junction of the left subclavian and left internal jugular veins. It acts as a channel for the collection of lymph from the portions of the body below the diaphragm and from the left side of the body above the diaphragm.
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia and Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier, Inc. All rights reserved.
com·mon he·pa·tic duct
[TA]the part of the biliary duct system that is formed by the confluence of right and left hepatic ducts. At the porta hepatis it is joined by the cystic duct to become the common bile duct.
Synonym(s): ductus hepaticus communis [TA], hepatocystic duct
Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012
hepatic duct
n.
The main excretory duct of the liver, which carries bile from the liver and joins the cystic duct to form the common bile duct.
The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company. Published by Houghton Mifflin Company. All rights reserved.
com·mon he·pa·tic duct
(kom'ŏn he-pat'ik dŭkt) [TA]The part of the biliary duct system that is formed by the confluence of the right and left hepatic ducts. At the porta hepatis it is joined by the cystic duct to become the bile duct.
Medical Dictionary for the Health Professions and Nursing © Farlex 2012