Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Post-Traumatic Frontal Mucocele Exceptional Cause and Frequent Recurrence
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Post-Traumatic Frontal Mucocele Exceptional Cause and Frequent Recurrence
Copyright:
Available Formats
Volume 5, Issue 8, August – 2020 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Post-Traumatic Frontal Mucocele:
Exceptional Cause and Frequent Recurrence
Hamid Khay, Mohammed Khoulali, Younes Dehneh, Lhamlili mohammed, Nabil Raouzi, Noureddine Oulali, Fayçal Moufid
Department of Neurosurgery, Mohammed VI university Hospital, Oujda, Morocco
Abstract:- The frontal mucocele is a benign pathology orbital wall with orbito-palpebral extension hiding and
characterized by its recurrence and is sometimes poor driving the eyeball downwards and outside. The patient
prognosis by the complications arising. We report the underwent surgery for drainage and marsupialization of the
case of a young man, followed for recurrent frontal pathological frontal mucosa associated with excision of the
mucocel, secondary to a sinus trauma. It is managed frontal mucocele membrane, mucocele content were
surgically with multiple reccurence. Our goal is to decry purulent, frontal sinus was aerated by milling the sinus
the appearance intraoperative an exceptional case walls. The patient also received intravenous antibiotic
mucocel frontal posttraumatic recurrent and therapy based on amoxicillin. The postoperative marked by
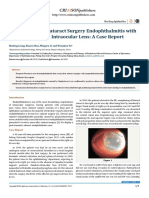
superinfected. a total recovery of the visual function and almost normal
eye-palpebral motility (Figure 2).
Keywords:- Post-Traumatic Mucocele, Surgery,
Recurrence, Infection. III. CONCLUSION
I. INTRODUCTION Surgical excision of mucocele and aeration the
pathological sinus is the treatment of choice for mucocele
Mucocele is a benign and rare cystic tumor, adults are and the recurrence one, mucocele is a benign tumor, but it
mainly affected. The frontal and / or ethmoidal mucocele, can cause serious locoregional complications due the delay
despite its histological benignity, has an aggressive in treatment or recurrence problems, antibiotics only
potential towards the local structures. It is due to a non- indicated in infected cases, as it was with our patient,
ventilatilated sinus. The post-traumatic cause is exceptional crânio-facial trauma is common in developing countries
and only one iatrogenic case reported following endonasal including Morocco, close follow-up is indicated to detected
surgery. Surgical treatment consists of excision of the cyst these serious complications.
and drainage of the causal sinus.1–3
REFERENCES
II. CASE REPORT
[1]. Aghakhanyan G, Lupi G, Frijia F, et al. Delayed Post-
A 38-years-old male patient with a history of nasal Traumatic Fronto-Ethmoidal Sinus Mucocele
fracture three years before, the patient was operated ten Evaluated with Short and Long TE MR Spectroscopy.
months ago for mucocele revealed by left eye Neuroradiol J. 26(6):693-698.
exophthalmos. The patient actually presents recurrence of [2]. Gupta M, Chauhan B, Gupta M, Gupta AK. Large
his exophthalmos. Clinical examination revealed left eye Frontoethmoidal Mucocele: Treatment and Review.
exophthalmos non pulsatile, non-axial and irreducible with doi:10.5005/JP-JOURNALS-10013-1171
limitation in eye movement upward and inward. Nasal [3]. Makihara S, Kariya S, Okano M, Naito T, Tsumura
endoscopy showed nasal mucosa inflamed absence of the M, Nishizaki K. Orbital complications of infected
left lower horn, synechiae on both side with purulent mucocele in the paranasal sinuses. Auris Nasus
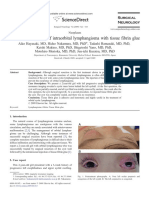
secretions (figure1). MRI And CT-scan of the nasal sinus Larynx. Published online June 11, 2020.
revealed a large left frontal mucocele lysing the superior doi:10.1016/j.anl.2020.05.012
IJISRT20AUG004 www.ijisrt.com 623
Volume 5, Issue 8, August – 2020 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Fig 1:- preoperative images (permission obtained from the patient for publication)
IJISRT20AUG004 www.ijisrt.com 624
Volume 5, Issue 8, August – 2020 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Fig 2:- operative and Postoperative images (permission obtained from the patient for publication)
Declarations:
Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable.
Consent for publication: Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials: Not applicable.
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding: None.
Authors’ contributions: Conception and design, Acquisition of data, Drafting the article, Reviewed submitted version of
manuscript and Approved the final version of the manuscript: all authors.
Acknowledgments: patient.
IJISRT20AUG004 www.ijisrt.com 625
You might also like
- Bio-Gro HyperGrowth Lean Mass FinalDocument17 pagesBio-Gro HyperGrowth Lean Mass FinalMarcelo Calderón Cruz80% (5)
- A. Desplat: Godzilla (2014) - Film Score AnalysisDocument18 pagesA. Desplat: Godzilla (2014) - Film Score AnalysisR.PercacciNo ratings yet
- Successful Treatment of Intraorbital Lymphangioma With Tissue Fibrin GlueDocument3 pagesSuccessful Treatment of Intraorbital Lymphangioma With Tissue Fibrin GlueIRANo ratings yet
- Supraclavicular Flap Reconstruction For Skin Defect After HugeParotid Region Lesion - Case ReportDocument6 pagesSupraclavicular Flap Reconstruction For Skin Defect After HugeParotid Region Lesion - Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Fibrous Hyperplasia - A Case ReportDocument4 pagesFibrous Hyperplasia - A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Management of Post-Operative Endophthalmitis: A ReviewDocument8 pagesManagement of Post-Operative Endophthalmitis: A ReviewIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis of Maxilla - A Rare Presentation CasDocument7 pagesOsteomyelitis of Maxilla - A Rare Presentation Casshehla khanNo ratings yet
- 10.nicula Cristina Final PRDocument4 pages10.nicula Cristina Final PRayub01No ratings yet
- Rare Case of A Conjunctival Cyst Formation in An Anophthalmic Socket of A 10 Years Old PatientDocument2 pagesRare Case of A Conjunctival Cyst Formation in An Anophthalmic Socket of A 10 Years Old PatientPeertechz Publications Inc.No ratings yet
- Management of Unsafe Type of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media With Extracranial Complications at A Tertiary Care CenterDocument6 pagesManagement of Unsafe Type of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media With Extracranial Complications at A Tertiary Care CenterLarasati Gilang Fuzi AstutiNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of A Defect Secondary To Sino-OrbitDocument5 pagesRehabilitation of A Defect Secondary To Sino-OrbitAnuRaveendranNo ratings yet
- Innovative Rehabilitation Approach Spectacle-Retained Orbital Prosthesis For Post-Mucormycosis Orbital DefectDocument5 pagesInnovative Rehabilitation Approach Spectacle-Retained Orbital Prosthesis For Post-Mucormycosis Orbital DefectInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Severe Fungal Cervicofacial Cellulitis From Otogenic Mucuromycosis Origin A Case ReportDocument4 pagesSevere Fungal Cervicofacial Cellulitis From Otogenic Mucuromycosis Origin A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 2012 - Frympas G.Document8 pages2012 - Frympas G.alejandra gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Management of Irritational Fibroma by Three Different Treatment Modalities - A Case SeriesDocument4 pagesManagement of Irritational Fibroma by Three Different Treatment Modalities - A Case SeriesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Rare Case of Periapical Healing in An Apically Extruding, Separated InstrumentDocument3 pagesA Rare Case of Periapical Healing in An Apically Extruding, Separated InstrumentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Nasal Glioma A Rare Case in Maxillofacial Surgery Practice A Case ReportDocument5 pagesNasal Glioma A Rare Case in Maxillofacial Surgery Practice A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cutis Verticis GyrataDocument4 pagesCutis Verticis GyrataChristianaNo ratings yet
- 2012 A Case Report of Mucormycosis of Faciotemporal Region Mimicking As Bacterial Necrotizing FasciitisDocument5 pages2012 A Case Report of Mucormycosis of Faciotemporal Region Mimicking As Bacterial Necrotizing FasciitisWaqar JeelaniNo ratings yet
- Aspergillosis Induced Osteomyelitis Involving The.125Document4 pagesAspergillosis Induced Osteomyelitis Involving The.125Andreea CiorneaNo ratings yet
- Surgical Treatment of Central Giant Cells Lesions With Right HemimaxillectomyDocument5 pagesSurgical Treatment of Central Giant Cells Lesions With Right HemimaxillectomyIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Household Orbital Trauma That Nearly Cost LifeDocument2 pagesHousehold Orbital Trauma That Nearly Cost LifeInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Rare Case of Myopericytoma of The Base of Right Index Finger Managed With en Bloc ExcisionDocument2 pagesA Rare Case of Myopericytoma of The Base of Right Index Finger Managed With en Bloc ExcisionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Superolateral Dislocation of Intact Mandibular Condyle A Rare Case SeriesDocument5 pagesSuperolateral Dislocation of Intact Mandibular Condyle A Rare Case SeriesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Conjunctivitis As A Manifestation of Wegener 'S GranulomatosisDocument5 pagesConjunctivitis As A Manifestation of Wegener 'S GranulomatosisAsd DsaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Efficacy of Laser Therapy in Peri-Implant It Is A ReviewDocument6 pagesClinical Efficacy of Laser Therapy in Peri-Implant It Is A ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Malleolar Fractures: Surgical Site Infection and Its Risk FactorsDocument18 pagesMalleolar Fractures: Surgical Site Infection and Its Risk FactorsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Application of Three-Dimensional Printing Technology in The Orbital Blowout Fracture ReconstructionDocument4 pagesApplication of Three-Dimensional Printing Technology in The Orbital Blowout Fracture Reconstructionstoia_sebiNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Sebaceous Gland Carcinoma of Upper Eyelid - A Case ReportDocument2 pagesRecurrent Sebaceous Gland Carcinoma of Upper Eyelid - A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Decrease in Visual Acuity As The Ini.3tial Clinical Presentation of Lung Adenocarcinoma A Case ReportDocument6 pagesDecrease in Visual Acuity As The Ini.3tial Clinical Presentation of Lung Adenocarcinoma A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- III Persistent Extraradicular Infection in Root-FilledDocument5 pagesIII Persistent Extraradicular Infection in Root-FilledAna Luísa MoraisNo ratings yet
- Msor 000504Document3 pagesMsor 000504MudrikahHaniyahNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Radiological Evaluations of Coronectomy For Impacted Mandibular Third MolarsDocument6 pagesClinical and Radiological Evaluations of Coronectomy For Impacted Mandibular Third MolarsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Granuloma Pyogenicum - A Case ReportDocument4 pagesGranuloma Pyogenicum - A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Study of Functional Outcome of Surgical Management of Proximal Humerus Fractures in A Tertiary Care HospitalDocument5 pagesStudy of Functional Outcome of Surgical Management of Proximal Humerus Fractures in A Tertiary Care HospitalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Delayed Complication of A Dry Socket Treatment-A Rare Case ReportDocument4 pagesA Delayed Complication of A Dry Socket Treatment-A Rare Case ReportI Gusti Ayu WulanNo ratings yet
- Ijo 69 1314Document4 pagesIjo 69 1314noonilNo ratings yet
- Cers Cadwell LucDocument3 pagesCers Cadwell LucVictorioStokNo ratings yet
- Regeneration of Periapical Bone in Surgical Endodontics: A Case ReportDocument7 pagesRegeneration of Periapical Bone in Surgical Endodontics: A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Post Covid 19 Mucoromycosis of MandibleDocument5 pagesPost Covid 19 Mucoromycosis of MandibleDr Yamuna RaniNo ratings yet
- Ocular Basidiobolomycosis A Case ReportDocument7 pagesOcular Basidiobolomycosis A Case ReportYUNA RATNA WULANSARINo ratings yet
- Analysis of Functional Disorders in Fractures of The Medial Wall of The Orbit in Hospitalised PatientsDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Functional Disorders in Fractures of The Medial Wall of The Orbit in Hospitalised PatientsCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- Atypical Case of Presumed Ocular Tuberculosis Presenting As Unilateral Occlusive VasculitisDocument4 pagesAtypical Case of Presumed Ocular Tuberculosis Presenting As Unilateral Occlusive VasculitisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Phacoemulsification Versus Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery in Hard NuclearDocument6 pagesPhacoemulsification Versus Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery in Hard NuclearRagni MishraNo ratings yet
- Reporte de Casos de MixomaDocument8 pagesReporte de Casos de Mixomacirugia.maxilo.melendezNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Health Sciences and ResearchDocument6 pagesInternational Journal of Health Sciences and ResearchDentist HereNo ratings yet
- Acfs 2019 00605 PDFDocument5 pagesAcfs 2019 00605 PDFChandra BudiNo ratings yet
- Depigmentation Using Scalpel and Diode Laser A Split Mouth Case ReportDocument5 pagesDepigmentation Using Scalpel and Diode Laser A Split Mouth Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Rhino Maxillary Mucormycosis During The Covid-19 Third Wave A Case ReportDocument4 pagesRhino Maxillary Mucormycosis During The Covid-19 Third Wave A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Sutureless and Glue Free Conjunctivo-Limbal Autograft in Primary Pterygium Surgery - Outcome S and Recurrence RateDocument8 pagesSutureless and Glue Free Conjunctivo-Limbal Autograft in Primary Pterygium Surgery - Outcome S and Recurrence RateThomas KweeNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation of A Post Covid Maxillectomy Defect With Definitive Obturator: A Case ReportDocument7 pagesRehabilitation of A Post Covid Maxillectomy Defect With Definitive Obturator: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- The Rapid Development of Squamous Cell Carcinoma On The Nasal Dorsum of A Patient Receiving Immunosuppressive TherapyDocument3 pagesThe Rapid Development of Squamous Cell Carcinoma On The Nasal Dorsum of A Patient Receiving Immunosuppressive TherapycarlakerengrNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontic Management of The Maxillary Defect Secondary To Mucormycosis: A Case ReportDocument9 pagesProsthodontic Management of The Maxillary Defect Secondary To Mucormycosis: A Case ReportIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Hydatidose of The Pelvis Simulating A Hemangioma: A Rare Location: About A CaseDocument2 pagesHydatidose of The Pelvis Simulating A Hemangioma: A Rare Location: About A CaseInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Surgical Ciliated Cyst of The Maxilla. Clinical Case: Jorge Cano, Julián Campo, Miguel Angel Alobera, Rafael BacaDocument4 pagesSurgical Ciliated Cyst of The Maxilla. Clinical Case: Jorge Cano, Julián Campo, Miguel Angel Alobera, Rafael BacaAhmad MustafaNo ratings yet
- Case Report Photochemical RetinopathyDocument5 pagesCase Report Photochemical RetinopathyAries YeungNo ratings yet
- Ijhs 12577+883 892Document10 pagesIjhs 12577+883 892hai1No ratings yet
- 2 Case Reports of Maxillofacial Osteomyelitis With Unique Presentations and Clinical ChallengesDocument8 pages2 Case Reports of Maxillofacial Osteomyelitis With Unique Presentations and Clinical ChallengesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Ridge Split Technique Using Piezosurgery - A Case ReportDocument6 pagesRidge Split Technique Using Piezosurgery - A Case ReportInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Novel Technique For Retention of Obturator Following Maxillectomy in Mucormycosis-A Case ReportDocument4 pagesA Novel Technique For Retention of Obturator Following Maxillectomy in Mucormycosis-A Case ReportBalwantNo ratings yet
- 2 Clinicopathological Comparative Vs Surgical 2018Document6 pages2 Clinicopathological Comparative Vs Surgical 2018solikin ikinNo ratings yet
- Zygomatic Implants: Optimization and InnovationFrom EverandZygomatic Implants: Optimization and InnovationJames ChowNo ratings yet
- Forensic Advantages and Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy Methods in Various Banknotes Analysis and The Observed Discordant ResultsDocument12 pagesForensic Advantages and Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy Methods in Various Banknotes Analysis and The Observed Discordant ResultsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaDocument6 pagesFactors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Study Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoDocument6 pagesStudy Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersDocument33 pagesCyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationDocument7 pagesBlockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Smart Health Care SystemDocument8 pagesSmart Health Care SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- An Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?Document8 pagesAn Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Unmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningDocument8 pagesUnmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Smart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyDocument19 pagesSmart Cities: Boosting Economic Growth Through Innovation and EfficiencyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldDocument6 pagesImpact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Parastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueDocument2 pagesParastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Visual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsDocument5 pagesVisual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Insights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesDocument8 pagesInsights Into Nipah Virus: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Therapeutic AdvancesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Compact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareDocument4 pagesCompact and Wearable Ventilator System For Enhanced Patient CareInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Quantifying of Radioactive Elements in Soil, Water and Plant Samples Using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) TechniqueDocument6 pagesQuantifying of Radioactive Elements in Soil, Water and Plant Samples Using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- An Analysis On Mental Health Issues Among IndividualsDocument6 pagesAn Analysis On Mental Health Issues Among IndividualsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Implications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewDocument6 pagesImplications of Adnexal Invasions in Primary Extramammary Paget's Disease: A Systematic ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Predict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningDocument2 pagesPredict The Heart Attack Possibilities Using Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Air Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMDocument8 pagesAir Quality Index Prediction Using Bi-LSTMInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsDocument5 pagesParkinson's Detection Using Voice Features and Spiral DrawingsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Teacher Reflective Practice and Students Engagement in The Public Elementary SchoolDocument31 pagesThe Relationship Between Teacher Reflective Practice and Students Engagement in The Public Elementary SchoolInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Keywords:-Ibadhy Chooranam, Cataract, Kann Kasam,: Siddha Medicine, Kann NoigalDocument7 pagesKeywords:-Ibadhy Chooranam, Cataract, Kann Kasam,: Siddha Medicine, Kann NoigalInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Investigating Factors Influencing Employee Absenteeism: A Case Study of Secondary Schools in MuscatDocument16 pagesInvestigating Factors Influencing Employee Absenteeism: A Case Study of Secondary Schools in MuscatInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Making of Object Recognition Eyeglasses For The Visually Impaired Using Image AIDocument6 pagesThe Making of Object Recognition Eyeglasses For The Visually Impaired Using Image AIInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix Dactylifera) Leaf Fiber As A Main Component in Making An Improvised Water FilterDocument11 pagesThe Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix Dactylifera) Leaf Fiber As A Main Component in Making An Improvised Water FilterInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Harnessing Open Innovation For Translating Global Languages Into Indian LanuagesDocument7 pagesHarnessing Open Innovation For Translating Global Languages Into Indian LanuagesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3Document9 pagesDiabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Advancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning For Accurate Health Index PrognosisDocument8 pagesAdvancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning For Accurate Health Index PrognosisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)Document2 pagesDense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Terracing As An Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains - CameroonDocument14 pagesTerracing As An Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains - CameroonInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- MH2732-Robotics Lab ManualDocument50 pagesMH2732-Robotics Lab Manualramzi ayadiNo ratings yet
- ED1021 - I/O Expander With UART Interface & Analog Inputs: PreliminaryDocument9 pagesED1021 - I/O Expander With UART Interface & Analog Inputs: PreliminaryMilan NovakovićNo ratings yet
- 1965 Elio R. Freni - Electrolytic Lead Refining in SardiniaDocument9 pages1965 Elio R. Freni - Electrolytic Lead Refining in SardiniaGeorgettaNo ratings yet
- Harmonization of HR Policies - RoughDocument119 pagesHarmonization of HR Policies - RoughFrancis SoiNo ratings yet
- Euroncap 2017 Audi q5 DatasheetDocument13 pagesEuroncap 2017 Audi q5 DatasheetCosmin AnculiaNo ratings yet
- External Otitis (OE)Document24 pagesExternal Otitis (OE)Hannah BLissNo ratings yet
- Wahabism - Bala SurajoDocument17 pagesWahabism - Bala SurajoAbu Muhammad50% (2)
- Mathematics (Course 18)Document24 pagesMathematics (Course 18)NickNo ratings yet
- Fuhs - Towards An Integral EpistemologyDocument39 pagesFuhs - Towards An Integral EpistemologyjmcmichaelNo ratings yet
- Project ChecklistDocument3 pagesProject Checklistarunurs1No ratings yet
- JNTU Old Question Papers 2007Document8 pagesJNTU Old Question Papers 2007Srinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Doxiadis, Constantinos (1968) EkisticsDocument556 pagesDoxiadis, Constantinos (1968) EkisticsCelje1234No ratings yet
- Grade 8 MAPEH ReviewerDocument4 pagesGrade 8 MAPEH ReviewerVictoria DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Osawa Catalogue 2021Document708 pagesOsawa Catalogue 2021lorenzo.lima1706No ratings yet
- 21 Day Fasting & Prayer 2022Document29 pages21 Day Fasting & Prayer 2022StephenNo ratings yet
- Case IH Farmall B - Brochure - 0717Document7 pagesCase IH Farmall B - Brochure - 0717nadeemmohamed555No ratings yet
- Commissioning Valve Product BrochureDocument14 pagesCommissioning Valve Product BrochureblindjaxxNo ratings yet
- Rebellion - Sagas of Iceland - The History of The Vikings Vol. 1Document28 pagesRebellion - Sagas of Iceland - The History of The Vikings Vol. 1Manuel Velasco100% (1)
- Tubular Flow ReactorDocument24 pagesTubular Flow ReactorluismiguelmmercadoNo ratings yet
- Watch Out For Flying Pumpkins: BOE Member PromotedDocument16 pagesWatch Out For Flying Pumpkins: BOE Member PromotedelauwitNo ratings yet
- Estimating Crack Widths in Steel Fibre-Reinforced ConcreteDocument12 pagesEstimating Crack Widths in Steel Fibre-Reinforced ConcreteRm1262No ratings yet
- Green Revolution: It's Acheivements and FailuresDocument24 pagesGreen Revolution: It's Acheivements and FailuresSingh HarmanNo ratings yet
- Use of Information Technology in The Flight Catering ServicesDocument32 pagesUse of Information Technology in The Flight Catering ServicesAbhiroop SenNo ratings yet
- 10-Msds-Remove Oil (Liquid)Document9 pages10-Msds-Remove Oil (Liquid)saddamNo ratings yet
- HYSYSDocument390 pagesHYSYSEfosaUwaifoNo ratings yet
- HINO Dutro Fault Codes List PDFDocument4 pagesHINO Dutro Fault Codes List PDFANH LÊNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Vegetasi Di Hutan Alam Dataran Rendah, Hutan Tanaman, Dan Lahan Pasca Tambang Nikel Di Kabupaten BombanaDocument6 pagesKarakteristik Vegetasi Di Hutan Alam Dataran Rendah, Hutan Tanaman, Dan Lahan Pasca Tambang Nikel Di Kabupaten BombanaWahyu AdistyaNo ratings yet
- Nokia 6131 NFCDocument5 pagesNokia 6131 NFCvetvetNo ratings yet