Abstract
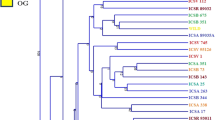
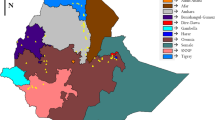
The extent and patterns of distribution of genetic variation among 80 sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) germplasm accessions from Ethiopia and Eritrea were investigated using RAPD with 20 oligonucleotide primers. The primers generated a total of 147 polymorphic bands across the 80 accessions with a mean of 7.35 bands per primer. Estimation of the extent of variation by the Shannon-Weaver diversity index revealed an intermediate level of overall variation (H = 53), although the levels varied among regions of origin of the accessions. Partitioning of the total variation revealed considerable variation (77%) within the region of origin of the accessions and the remainder (23%) among regions of origin. Similarly, a large portion (94%) of the total variation was found within the adaptation zones compared to among the adaptation zones (6%). The results suggest a weak differentiation of the sorghum material both on regional and agro-ecological bases, which could be ascribed to the high rate of outcrossing in cultivated sorghum and its free natural hybridization with its wild and weedy relatives, as well as to seed movement by humans. The average genetic dissimilarity was found to be 36% among the 80 accessions and 13% among the 15 regions of origin. Cluster analysis failed to group accessions of the same region or the same adaptation zone, which further confirmed the weak differentiation of the material studied. The clustering pattern of the regions of origin was broadly concordant with previous clustering patterns obtained using morphological characters, in which regions with broad agro-climatic conditions were grouped together.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldrich, P.R. & J. Doebley, 1992. Restriction fragment variation in the nuclear and chloroplast genomes of cultivated and wild Sorghum bicolor. Theor. Appl. Genet. 85: 293-302.
Aldrich, P.R., J. Doebley, K.F. Schertz & A. Stec, 1992. Patterns of allozyme variation in cultivated and wild Sorghum bicolor. Theor. Appl. Genet. 85: 451-460.
Ayana, A. & E. Bekele, 1998. Geographical patterns of morphological variation in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) germplasm from Ethiopia and Eritrea: Qualitative characters. Hereditas 129: 195-205.
Ayana, A. & E. Bekele, 1999. Multivariate analysis of morphological variation in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) germplasm from Ethiopia and Eritrea. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 46: 387-384.
Beer, S.R., J. Goffreda, T.D. Phillips, J.P. Murphy & M.E. Sorrells, 1993. Assessment of genetic variability in Avena sterilis using morphological traits, isozymes, and RFLPs. Crop Sci. 33: 1386-1393.
Bogyo, T.P., E. Porceddu & P. Perrino, 1990. Analysis of sampling strategies for collecting genetic material. Econ. Bot. 34: 160-174.
Bretting, P.K. & M.P. Widrlechner, 1996. Genetic markers and plant genetic resources management. Plant Breed. Rev. 13: 11-86.
Brown, A.H.D., 1989. Core collections: a practical approach to genetic resources management. Genome 31: 818-824.
Brunk, C.F., K.C. Jones & T.W. James, 1979. Assay for nanogram quantities of DNA in cellular homogenates. Anal. Biochem. 92: 497-500.
Chalmers, K.J., R.Waugh, J.I. Sprent, A.J. Simons & W. Powell, 1992. Detection of genetic variation between and within populations of Gliricidia sepium and G. maculata using RAPD markers. Heredity 69: 465-472.
Cui, Y.X., G.W. Xu, C.W. Magill, K.F. Schertz & G.E. Hart, 1995. RFLP-based assay of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench genetic diversity. Theor. Appl. Genet. 90: 787-796.
de Oliveira, A.C., T. Richter & J.L. Bennetzen, 1996. Regional and racial specificities in sorghum germplasm assessed with DNA markers. Genome 39: 579-587.
Deu, M., D. Gonzalez-de-Leon, J.C. Glaszmann, I. Degremont, J. Chantereau, C. Lanaud & P. Hamon, 1994. RFLP diversity in cultivated sorghum in relation to racial differentiation. Theor. Appl. Genet. 88: 838-844.
Doggett, H., 1988. Sorghum, 2nd ed., Longman, U.K.
Doggett, H., 1991. Sorghum history in relation to Ethiopia. In: Engels, J.M.M., J.G. Hawkes & M. Worede (Eds.), Plant Genetic Resources of Ethiopia, pp. 140-159, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Doggett, H. & K.E. Prasada Rao, 1995. Sorghum. In: J. Smartt & N.W. Simmonds (Eds.) Evolution of Crop Plants, 2nd ed., pp 140-159, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Faris, M.A., M.D.E. Lira, A.F. Veiga & S.L. De, 1979. Stability of sorghum midge resistance. Crop Sci. 19: 577-588.
Gebrekidan, B., 1973. The importance of the Ethiopian sorghum germplasm in the world sorghum collection. Econ. Bot. 23: 442-445.
Gebrekidan, B., 1981. Salient features of the sorghum breeding strategies used in Ethiopia. Eth. J. Agric. Sci. 3: 97-104.
Gebrekidan, B. & Y. Kebede, 1979. The traditional culture and yield potentials of the Ethiopian high lysine sorghums. Eth. J. Agric. Sci. 1: 29-40.
Gepts, P., 1995. Genetic markers and core collections. In: T. Hodgkin, A.H.D. Brown, Th.J.L. van Hintum & E.A.V. Morales (Eds.), Core Collections of Plant Genetic Resources, pp. 127-146, International Board of Plant Genetic Resources Institute (IBPGRI), A Wiley-Sayce Publication.
Gower, J.C., 1971. A general coefficient of similarity and some of its properties. Biometrics 27: 857-871.
Hamrick, J.L. & J.W. Godt, 1997. Allozyme diversity in cultivated crops. Crop Sci. 37: 26-30.
Harlan, J.R., 1992. Crops and Man, 2nd ed., Am. Soc. Agron., Crop Sci. Soc. Am., Madison, WI.
Hutchenson, K., 1970. A test for comparing diversities based on the Shannon formula. J. Theor. Biol. 29: 151-154.
Junghans, H. & M. Metzlaff, 1990. A simple and rapid method for the preparation of total DNA. Biotechniques 8: 176.
Kazan, K., J.M. Manners & D.F. Cameron, 1993. Inheritance of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers in an interspecific cross in the genus Stylosanthes. Genome 36: 50-56.
Kebede, Y., 1991. The role of Ethiopian sorghum germplasm resources in national breeding programme. In: J.M.M. Engels, J.G. Hawkes & M. Worede (Eds.), Plant Genetic Resources of Ethiopia, pp. 315-322, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
King, L.M. & B.A. Schaal, 1989. Ribosomal-DNA variation and distribution in Rudbeckia missouriensis. Evolution 43: 1117-1119.
Lee, M., 1995. DNA markers and plant breeding programmes. Adv. Agron. 55: 265-344.
Liu, Z. & G.R. Furnier, 1993. Comparison of allozyme, RFLP, and RAPD markers for revealing genetic variation within and between trembling aspen and bigtooth aspen. Theor. Appl. Genet. 87: 97-105.
Lu, M.Z., A.E. Szmidt & X.R. Wang, 1995. Inheritance of RAPD fragments in haploid and diploid tissues of Pinus sylvestris (L.). Heredity 74: 582-589.
Lynch, M., 1988. Estimation of relatedness by DNA fingerprinting. Mol. Biol. Evol. 5: 584-599.
Lynch, M. & M.G. Milligan, 1994. Analysis of population genetic structure with RAPD markers. Mol. Ecol. 3: 91-99.
Mann, J.A., C.T. Kimber & F.R. Miller, 1983. The origin and early cultivation of sorghums in Africa. Texas Agric. Expt. Sta. Bull. No. 1454.
Mengesha, M.H., 1975. Crop germplasm diversity resources of Ethiopia. In: O.H. Frankel & J.G. Hawkes (Eds.), Crop Genetic Resources for Today and Tomorrow, pp. 449-453, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Menkir, A., P. Goldsbrough & G. Ejeta, 1997. RAPD based assessment of genetic diversity in cultivated races of sorghum. Crop Sci. 37: 564-569.
Morden, C.W., J. Doebley & K.F. Schertz, 1990. Allozyme variation among the spontaneous species of Sorghum section Sorghum (Poaceae). Theor. Appl. Genet. 80: 296-304.
Morden, C.W., Doebley, J.F. & K.F. Schertz, 1989. Allozyme variation in Old World races of Sorghum bicolor (Poaceae). Am. J. Bot. 76: 247-255.
Mumm, R.H. & J.W. Dudley, 1995. A PC SAS computer program to generate a dissimilarity matrix for cluster analysis. Crop Sci. 35: 925-927.
Nei, M., 1972. Genetic distance between populations. Am. Nat. 106: 283-292.
Nei, M., 1978. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89: 583-590.
Nevo, E., B. Baum, A. Beiles & D.A. Johnson, 1998. Ecological correlates of RAPD DNA diversity of wild barley, Hordeum spontaneum, in the Fertile Crescent. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 45: 151-159.
Newbury, H.J. & B.V. Ford-Lloyd, 1993. The use of RAPD for assessing variation in plants. Plant Growth Regul. 12: 413-451.
Pammi, S., K.F. Schertz, G. Xu, G. Hart & J.E. Mullet, 1994. Random-amplified-polymorphic DNA markers in sorghum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 89: 80-88.
Prasada Rao, K.E., M.H. Mengesha & V.G. Reddy, 1989. International use of a sorghum germplasm collection. In: A.H.D. Brown, D.R. Marshall, O.H. Frankel & T.J. Williams (Eds.), The Use of Plant Genetic Resources, pp. 49-67, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Rieseberg, L.H., 1996. Homology among RAPD fragments in interspecific comparisons. Mol. Ecol. 5: 99-105.
Rohlf, F.J., 1993. NTSYS-PC Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 1.80, Exeter Publ., Ltd., Setauket, NY.
Shechter, Y. & J.M.J. de Wet, 1975. Comparative electrophoresis and isozyme analysis of seed proteins from cultivated races of sorghum. Am. J. Bot. 62: 254-261.
Singh, R. & J.D. Axtell, 1973. High lysine mutant gene (hl) that improves protein quality and biological value of sorghum. Crop Sci. 13: 535-539.
Singh, S.P., 1985. Sources of cold tolerance in grain sorghum. Can. J. Plant Sci. 65: 251-257.
Singh, S.P., J.A. Gutierrez, A. Molina, C. Urrea & P. Gepts, 1991. Genetic diversity in cultivated common bean: II. Marker-based analysis of morphological and agronomic traits. Crop Sci. 31: 23-29.
Skroch, P. & J. Nienhuis, 1995. Impact of scoring error and reproducibility of RAPD data on RAPD based estimates of genetic distance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 91: 1086-1091.
Skroch, P.W., J. Nienhuis, S. Beebe, J. Tohme & F. Pedraza, 1998. Comparison of Mexican common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) core and reserve germplasm collections. Crop Sci. 38: 488-496.
Smith, J.S.C. & O.S. Smith, 1992. Fingerprinting crop varieties. Adv. Agron. 47: 85-140.
Sneath, P.H.A. & R.R. Sokal, 1973. Numerical Taxonomy, W.H. Freeman and Co., San Francisco.
Tao, Y., J.M. Manners, M.M. Ludlow & R.G. Henzell, 1993. DNA polymorphism in grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.)Moench). Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: 679-688.
Teshome, A., B.R. Baum, L. Fahrig, J.K. Torrance, T.J. Arnason & J.D. Lambert, 1997. Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) landrace variation and classification in north Shewa and South Welo, Ethiopia. Euphytica 97: 255-263.
Tingey, S.V. & J.P. del Tufo, 1993. Genetic analysis with random amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Plant Physiol. 101: 349-352.
Tinker, N.A., M.G. Fortin & D.F. Mather, 1993. Random amplified polymorphic DNA and pedigree relationships in spring barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 85: 976-984.
Vierling, R.A. & H.T. Nguyen, 1992. Use of RAPD markers to determine the genetic diversity of diploid wheat genotypes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 84: 835-838.
Vierling, R.A., Z. Xiang, C.P. Joshi, M.L. Gilbert & H.T. Nguyen, 1994. Genetic diversity among elite Sorghum lines revealed by restriction fragment length polymorphisms and random amplified polymorphic DNAs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 87: 816-820.
Wachira, F.N., R. Waugh, C.A. Hackett & W. Powell, 1995. Detection of genetic diversity in tea (Camellia sinensis) using RAPD markers. Genome 38: 201-210.
Williams, J.G.K., M.K. Hanafey, J.A. Rafalski & S.V. Tingey, 1993. Genetic analysis using RAPD markers. Methods Enzymol. 218: 704-740.
Williams, J.G.K., R.A. Kubelik, K.J. Livak, J.A. Rafalski & S.V. Tingey, 1990. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 18: 6531-6535.
Yang, W., A.C. de Oliveira, I. Godwin, K.F. Schertz & J.L. Bennetzen, 1996. Comparison of DNA marker technologies in characterizing plant genome diversity: Variability in Chinese sorghums. Crop Sci. 36: 1669-1676.
Zhang, Q., M.A. Saghai Maroof & A. Kleinhofs, 1993. Comparative diversity of analysis of RFLPs and isozymes within and among populations of Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum. Genetics 134: 909-916.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayana, A., Bryngelsson, T. & Bekele, E. Genetic variation of Ethiopian and Eritrean sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) germplasm assessed by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution 47, 471–482 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008751721825
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008751721825