Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Comparative Study of Albendazole and Euphorbia Thymifolia For Anthelmintic Activity
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Comparative Study of Albendazole and Euphorbia Thymifolia For Anthelmintic Activity
Copyright:
Available Formats
Volume 8, Issue 1, January – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
The Comparative Study of Albendazole and
Euphorbia thymifolia for Anthelmintic Activity
Pratiksha S. Dhembare*, Pratiksha K. Dange, Rohan A. Dhamane, Sanket B. Chopade, Sandeep R.Kane,Shrinivas K. Mohite
Rajarambapu College of Pharmacy, Kasegaon, Maharashtra, India
Abstract:- Nanoparticles are defined as particles with one sometimes known as anthelmintics, are used to eliminate
or more dimensions and sizes between one and one internal parasites like helminthes and other parasitic worms
hundred nanometers (nm) by ISO and ASTM standards. from the body without causing serious harm to the host. [6, 7]
Due to their special qualities, silver nanoparticles have a .They are sometimes called insecticides or anthelmintics
wide range of uses, including antibacterial, anticancer, (stunning) or as "Insecticide" (insecticide). Helminthiasis, an
larvicidal, catalytic, and wound healing processes. Any infection caused by helminthes, is treated with anthelmintics.
medication that treats parasitic worm-related infections
is known as an anthelmintic (helminthes). An established Many worm infestations can be treated with
anthelmintic medication is Albendazole. Certain albendazole, commonly referred to as albendazolum.
tapeworm infections are treated with the drug Giardiasis, whipworm, filariasis, neurocysticercosis,
Albendazole (such as neurocysticercosis and hydatid cysticercosis, pinworm, ascariasis, etc. conditions, can all be
disease). The centrifugation method wasused for 3 hours effectively treated with it. Threadworms, roundworms,
and 34 hours, respectively, to manufacture silver nanoparticles whipworms, tapeworms, and hookworms can all be
from Albendazole and Euphorbia thymifolia. Pheretima successfully treated with albendazole. [8, 9]
posthuma, an Indian earthworm, was tested for anthelmintic
activity using Albendazole and Euphorbia thymifolia Broad-spectrum anthelmintics like albendazole and
nanoparticles in ethanol. The results were stated for Euphorbia thymifolia suppress tubulin polymerization, which
paralysis and bacterial death time after monitoring various leads to the loss of cytoplasmic microtubules in the intestines
concentrations of both Albendazole and Euphorbia of nematode worms, which in turn affects the worm's nervous
thymifolia. Both plants' dose-dependent activity was seen. system and causes energy exhaustion. The parasite becomes
However, the synthetic medicineAlbendazole exhibits greater immobilized as a result and eventually dies. [10, 11]
activity than the herbal drug Euphorbia thymifolia. It was
determined thatboth the synthetic and natural medicines had II. MATERIAL AND METHODS
anthelmintic activity, with Albendazole having more of aneffect
than Euphorbia thymifolia. Anthelmintic Assay
Keywords:- Nanoparticle Synthesis, Silver Nanoparticles, A. Preparation of plant extract:
Albendazole, Euphorbia Thymifolia, and Anthelmintic A synthetic medicine called albendazole was broken
Activity. down into a powder, which was then incubated with AgNO3
in alcohol for three hours. The medication powder was further
I. INTRODUCTION dilutedin distilled water to 0.01, 0.02, and 0.03 mg/mL.
Nanotechnology is an important area of modern Euphorbia thymifolia plant extract was treated with
research dealing with the synthesis, planning, and AgNO3 in alcohol for 24 hours. The plant extract was further
manipulation of particle formation from 1 to 100 nm in size. diluted in distilled water to 0.01, 0.02, and 0.03 mg/ml.
[1,2,3]
Special properties such as chemical stability, excellent
conductivity, catalytic activity and most importantly B. Worms’ collection:
antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal activity make it suitable In Rajarambapu Vermicomposting Project,
for incorporation into composite fibers, materials for Rajaramnagar, Islampur, Sangli, Maharashtra, India, and
cryogenic superconducting technology, cosmetics, food from Dr. S. U. Patil, Pheretima posthuma (Indian earthworm)
industry, etc. can do. Electronic devices,silver nanoparticles was collected. This earthworm was verified by Smt.
are typical products in the field of nanotechnology. [4, 5] Kusumtai Rajarambapu Patil, Head of the Zoology
Department at Kanya Mahavidyalaya in Islampur, Sangli,
Silver "acts" as an antiseptic and exhibits broad biocidal and Maharashtra.
efficacy against microorganisms in biomedical applications,
including wound dressings, topical creams, antiseptic sprays, C. Anthelmintic Assay:
and added to fabrics. This is accomplished by disrupting their P. posthuma, an earthworm, was split into seven groups,
unicellular membrane, which in turn interferes with their each containing two earthworms of the same size (in
enzymatic activities. The detection and therapy of cancer also triplicates) and was then released into 30 ml of the
employ these silver nanoparticles with success. experimental formulation kept in the petri dish. The first
Antiparasitic medications known as anthelmintics,
IJISRT23JAN715 www.ijisrt.com 550
Volume 8, Issue 1, January – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
group served as the control and was just given regular After estimating the mean paralysis duration, the time of
distilledwater treatment. The second, third, and fourth groups death was measured in seconds to make sure that the
consisted of various concentrations of the synthetic earthworms did not move when shaken or when an external
medication albendazole (0.01, 0.02, and 0.03 mg/mL). The stimulus was applied by submerging the immobile worms in
herbal medication extracts of Euphorbia thymifolia were used 500°C hot water. The death of the worms was indicated by
in the fifth, sixth, and seventh groups in varying their immobility, the appearance of a white secretion, the
concentrations (0.01, 0.02, and 0.03). Before beginning the fading of the colour surrounding their bodies. The length of
experiment, each test solution wasfreshly made. [12, 13, 14, death andparalysis were specified in minutes.
15]
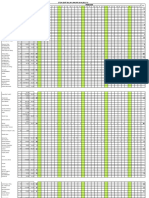
Table 1:- Comparative study of Albendazole and Euphorbia for Antihelmintic activity
IJISRT23JAN715 www.ijisrt.com 551
Volume 8, Issue 1, January – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
III. RESULTS
Fig 1. CONTROL Fig 2. ALBENDAZOLE (0.01ML)
Fig 3 .ALBENDAZOLE (0.02 ML) Fig 4. ALBENDAZOLE (0.03 ML)
Fig 5. EUPHORBIA THYMIFOLIA (0.01 ML) Fig 6. EUPHORBIA THYMIFOLIA (0.02 ML)
IJISRT23JAN715 www.ijisrt.com 552
Volume 8, Issue 1, January – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Fig 7. EUPHORBIA THYMIFOLIA (0.03 ML)
The ethanolic extract contains saponins, steroids, The adult Indian earthworm Pheretima posthuma
alkaloids, tannins, and flavonoids, according to preliminary responds similarly to intestinal parasites in response to
phytochemical screening. It is observed that standard anthelmintic drugs and is readily available, which was used
albendazole shows potent anthelmintic activity while in this study to compare the anthelmintic activity of the
Euphorbia thymifolia takes a long time to kill worms. synthetic drug Albendazole and the herbal drug Euphorbia
Albendazole causes paralysis within 2–3 minutes, while the thymifolia. Comparing the anthelmintic activity of the herbal
death of worms takes place in 3–4 minutes. Paralysis occurs medication Euphorbia thymifolia extract to that of the
in 2-2.5 minutes in Euphorbia thymifolia, while worm death synthetic drug Albendazole, the former showed less. The
occurs in 4-4.5 minutes. [16, 17] highest anthelmintic activity in ethanolic extract is caused by
the presence of alkaloids and tannins. As concentrations were
IV. DISCUSSION raised, ethanolic extracts became more effective as an
anthelmintic. When compared to the usual reference
The chemical makeup of each plant is unique, and even medicine albendazole, Bendgude et al. found that ethanol
within the same plant, the chemical makeup changes from extracts significantly shortened nematode paralysis and death
one area of the plant to another. Depending on their solubility, time in a dose-dependent manner Alkaloids, tannins, phenols,
the plant's phytochemicals can be dissolved in ethanol. As a and other phytochemicalsare said to have strong anthelmintic
result, ethanolic extracts of the herbal plant Euphorbia properties, while alkaloids are said to operate on the
thymifolia were chosen to manufacture with the common earthworm's nervous system to paralyze it. Tannins have been
synthetic medicine Albendazole. The results of the current found to uncouple oxidative phosphorylation, which
study indicate that the ethanolic solvent extract of Euphorbia interferes with worm energy production, or they can attach to
thymifolia include a variety of phytochemicals, including the free protein of the GIT and kill worms. Inhibition of
alkaloids, glycosides, coumarin, saponins, sterols, tubulin polymerization, prevention of glucose uptake, and
polyphenols, flavonoids, and tannins. The ethanolic extract of damage to nematode mucopolysaccharide membranes are
the common medicine Albendazole had more phytochemicals three ways phytochemicals may act collectively or singly.
and bioactive components as a result of which it shown the
highest anthelmintic activity. Secondary metabolites or V. CONCLUSION
phytochemicals typically exist in complicated combinations
that vary depending on the organs and stages of development The silver nanoparticles of the common synthetic
of the plant. For Euphorbia thymifolia to be used as medicine Albendazole exhibit powerful anthelmintic activity
effectively as possible in medicine, knowledge of the when compared to the silver nanoparticles of the herbal
photochemical components present and albendazole will be Euphorbia thymifolia, according to a comparative research of
very helpful. According to reports, phytochemicals found in the two substances. Alkaloids, glycosides, tannins, sterols,
plants are important sources of anti- inflammatory, antiviral, flavonoids, and polyphenols are some examples of the
anti-tumor, antibacterial, and anthelmintic compounds. As a phytochemical components that contribute to albendazole's
result, they are used as components in both allopathic and effectiveness as an anthelmintic.
alternative medical systems. [18]
IJISRT23JAN715 www.ijisrt.com 553
Volume 8, Issue 1, January – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
We can see that normal albendazole induces paralysis in
2-3 minutes and death in 3–4 minutes when we examine the [14]. N Mondel, S Mondel, P Ghosh, C Ghosh, S Das, and S
paralysis and death times of worms against both of these Chaterjee are among the authors. The Pharma
medications. Euphorbia thymifolia experiences paralysis in Innovation Journal 2019;8(2):464468, Olenlandia
2-2.5 minutes and worm death in 4-4.5 minutes. As a result, corymbosa Linn: Botanical Feature, Phytochemical,
we draw the conclusion that the active phytochemical and Pharmacological Overviews.
components, such as tannins and glycosides, which inhibit [15]. Pharmacognosy, 12th edition, ELBS Publications,
tubulin polymerization, obstruct glucose uptake, and harm the London, 1985: 126.
worms' mucopolysaccharide membrane, exposing the outer [16]. Trease GE, Evans WC."Antimicrobial alkaloids from
layer and restricting movement, potentially leading to Euphorbia thymifolia," Pak Sci Indian Res., 8: 293,
paralysis and eventual death.[19, 20] 1965.
[17]. Chapman & Hall, London, 1973, Phytochemical
REFERENCES Methods: A Guide to Modern Techniques of Plant
Analysis, 3: 182-189.
[1]. H. Korbekandi, Iravani Silver Nanoparticles, and [18]. Euphorbia Thymifolia's Anti-oxidant and Anti-Viral
Nanoparticle Distribution Editor Hashim Abbass A., Activities, Journal of Biomedical Science, 9(6): 656664,
Intec, 2012, ISBN 978-953-51-0615-9. 2002. Yang CM, Lin CM, Cheng HY, and Lin CC.
[2]. "Preparation and characterisation of electrospun [19]. The hydromethanolic extract of Mikania Scandens (L)
PLGA/silver composite nanofibers for biomedical wild leaves has analgesic and antioxidant activities,
applications" by Khalil, H. Fouad, T. Elsarnagawy, and according to Hasan, S.M.R., Jamila, M., Majumder,
F.N. Almajhdi Int J Electrochem Sci, 8, 3483-3493 M.M., Akter, R., Hossain, M.M., Mazumder, M.E.H.,
(2013). Alam, M.A., Jahangir, R., Rana, M.S., and Rahman,
[3]. B. Viswanathan and J. Kaviya, "Green production of American Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology,
silver nanoparticles using D-sorbitol and Polyalthia Vol. 4, No. 1, pp. 1–7.
longifolia leaf extract," J Nanotech (2011), 1–5. [20]. Physico-chemical and antimicrobial research of
[4]. Ahmad, P. Mukherjee, S. Senapati, D. Mandal, M. I. polyherbal formulation 1-3 in International Journal of
Khan, R. Kumar, and M. Sastry, "Extracellular Comprehensive Pharmacy, by Mohanty, A., Das, C.,
production of silver nanoparticles utilising the fungus Dash, S., and Sahoo, D.C..
Fusarium oxysporum," Colloids Surf B: Bio Interfaces,
28, 313–318 (2003).
[5]. Metal-accumulating bacteria and their promise for
materials science: Klaus-Joerger, R. Joerger, E.Olsson,
and C. Granqvist, "Bacteria as workers in the living
factory," Trends Biotechnology, 19 (2001), 15-20.
[6]. A. Velea, A. Lorinczi, and Popescu, "Biogenic synthesis
of nanoparticles," Dig. J. Nanomater. Bios., 5(4) (2010),
1035–1040.
[7]. In Green Chem, 11 (2009), 926–930, Baruwati, V.
Polshettiwar, R.S. Varma, and glutathione promoted
rapid green production of silver nanoparticles in water
using microwaves.
[8]. "Albendazole" in Plumb's Veterinary Drug Handbook,
Plumb DC (7th). Wiley, Stockholm, Wisconsin; Ames,
Iowa ISBN 978-0-470-95964-0, 19–21."
[9]. Albendazole." com. The American Society of Health-
System Pharmacists on September 23, 2015.
[10]. Junquera Safety summary for veterinary use on dogs,
cats, cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, and poultry with regard
to albendazole toxicity, poisoning, intoxication,
overdose, and antidote.
[11]. Sampson T, Waller DG (June 4, 2017). Elsevier Health
Sciences, Medical Pharmacology and Therapeutics E-
Book, p. 616. ISBN 978-0-7020-7190-4."
[12]. Manorma K. and Preety S. J. Curr. Science "Ethano
botanical studies of the family Euphorbiaceae: A
review seminar." 2011; 16(1):7578.
[13]. Ci dian Zhong Yao, published in 1986 by the Shanghai
Science and Technology Press:13
IJISRT23JAN715 www.ijisrt.com 554
You might also like
- Jim Humble - The SolutionDocument113 pagesJim Humble - The SolutionA A100% (6)
- RA 11712 Benefits and Allowances for HCWsDocument24 pagesRA 11712 Benefits and Allowances for HCWsgenNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Plants With Anti-Snake Venom Property: A ReviewDocument5 pagesMedicinal Plants With Anti-Snake Venom Property: A ReviewCol Ran SinghNo ratings yet
- HSI G2020 UniversalUpdateFinalv4Document44 pagesHSI G2020 UniversalUpdateFinalv4Ralph Loris Lagas RN100% (1)
- Dror Paley - Principles of Deformity Correction (2002, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg) - 1-100Document100 pagesDror Paley - Principles of Deformity Correction (2002, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg) - 1-100Wilker AraújoNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterisation, Properties and ApplicationsFrom EverandEnzyme Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterisation, Properties and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Screening of Antibacterial Antituberculosis and Antifungal Effects of Lichen Usnea Florida and Its Thamnolic Acid ConstituentDocument6 pagesScreening of Antibacterial Antituberculosis and Antifungal Effects of Lichen Usnea Florida and Its Thamnolic Acid ConstituentJoe ScaliaNo ratings yet
- Larvicidal Activity of Leucas Aspera Against The Larvae of Anopheles, Aedes Aegypti and Culex QuinquefasciatusDocument7 pagesLarvicidal Activity of Leucas Aspera Against The Larvae of Anopheles, Aedes Aegypti and Culex QuinquefasciatusIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological & Anti-Fungal Activity of Garlic (Allium Sativum)Document5 pagesPharmacological & Anti-Fungal Activity of Garlic (Allium Sativum)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Husna 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1467 012014Document8 pagesHusna 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1467 012014hanna eloreeNo ratings yet
- Oldenlandia UmbellataDocument4 pagesOldenlandia UmbellataugoNo ratings yet
- 9 III March 2021Document10 pages9 III March 2021IJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Larvicidal Activity of Celosin A, A Novel Compound Isolated From Celosia Argentea LinnDocument6 pagesLarvicidal Activity of Celosin A, A Novel Compound Isolated From Celosia Argentea LinnInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Antidermatophytic Activity of Acacia Concinna: V. Natarajan and S. NatarajanDocument2 pagesAntidermatophytic Activity of Acacia Concinna: V. Natarajan and S. NatarajanRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Studies On Macroscopic, Microscopic, and TLC Based Phytochemical Analysis of Euphorbia Thymifolia Linn.Document8 pagesStudies On Macroscopic, Microscopic, and TLC Based Phytochemical Analysis of Euphorbia Thymifolia Linn.SSR-IIJLS JournalNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Bioactivity Assay of Ulin (Eusideroxylon Zwageri Teijsm. & Binn) Plant Bark Extract Against Staphylococcus Aureus BacteriaDocument3 pagesAntibacterial Bioactivity Assay of Ulin (Eusideroxylon Zwageri Teijsm. & Binn) Plant Bark Extract Against Staphylococcus Aureus BacteriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 186 PDFDocument4 pages186 PDFMonyet...No ratings yet
- 2018-Maybe Use-Rhyzophora Stylosa (Mangrove)Document12 pages2018-Maybe Use-Rhyzophora Stylosa (Mangrove)DwiNo ratings yet
- Secondary Metabolite From EculauptusDocument10 pagesSecondary Metabolite From EculauptusRahul MandalNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 3 HipersensitivitasDocument5 pagesJurnal 3 HipersensitivitasDolphin PangalaNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial and antifungal properties of Solanum torvumDocument8 pagesAntibacterial and antifungal properties of Solanum torvumw vanayaNo ratings yet
- Abalaka Et Al. 2012Document5 pagesAbalaka Et Al. 2012Leandro DouglasNo ratings yet
- Sunita Dashrath Bansod, Manisha Subrashrao Bawaskar, Aniket Krishnarao Gade, Mahendra Kumar RaiDocument7 pagesSunita Dashrath Bansod, Manisha Subrashrao Bawaskar, Aniket Krishnarao Gade, Mahendra Kumar Raisasibhushanarao poolaNo ratings yet
- Teknik PemisahanDocument7 pagesTeknik PemisahanOki Rudy SetyawannNo ratings yet
- 24 Vol.2 8 IJPSR 696 Paper 8Document9 pages24 Vol.2 8 IJPSR 696 Paper 8Cicy IrnaNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Analysis of Hyptis Suaveolens Extract and Its Effects On The Growth of Disease-Causing ParasitesDocument6 pagesPhytochemical Analysis of Hyptis Suaveolens Extract and Its Effects On The Growth of Disease-Causing ParasitesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Anti-Bacterial Activity of Medicinal PlantsDocument4 pagesComparative Analysis of Anti-Bacterial Activity of Medicinal PlantsLeandro DouglasNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical and Antibacterial Activity Screening of Acalypha Indica and Ocimum TenuiflorumDocument9 pagesPhytochemical and Antibacterial Activity Screening of Acalypha Indica and Ocimum TenuiflorumIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- 05 Iajps05092020Document7 pages05 Iajps05092020iajpsNo ratings yet
- (18469558 - Acta Pharmaceutica) Anthelmintic Activity of Praziquantel and Spilanthes Acmella Extract On An Intestinal Cestode ParasiteDocument10 pages(18469558 - Acta Pharmaceutica) Anthelmintic Activity of Praziquantel and Spilanthes Acmella Extract On An Intestinal Cestode ParasiteDiego NamucheNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Effect of Acronychia Pedunculata Fresh Extract Against Staphylococcus Aureus A Study in VitroDocument5 pagesAntibacterial Effect of Acronychia Pedunculata Fresh Extract Against Staphylococcus Aureus A Study in VitroEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Activity of Achyranthus AsperaDocument4 pagesEvaluation of Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Activity of Achyranthus AsperaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical Studies and Anti-Bacterial Activities of Amaranthus Spinosus.LDocument6 pagesPhytochemical Studies and Anti-Bacterial Activities of Amaranthus Spinosus.LdanilriosNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in Lagerstroemia Speciosa (L.) Pers and Their Antimicrobial ActivitiesDocument5 pagesBiosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles in Lagerstroemia Speciosa (L.) Pers and Their Antimicrobial ActivitiesKristine AllejeNo ratings yet
- Fungicidal Property of Andrographis Paniculata Extract On Fungal Organisms From Citrullus Colocynthis (L.) Schrad (Melon Seeds)Document6 pagesFungicidal Property of Andrographis Paniculata Extract On Fungal Organisms From Citrullus Colocynthis (L.) Schrad (Melon Seeds)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activity On Leaves Extract of Croton Sparsiflorious and Jatropha GossipifoliaDocument4 pagesAntibacterial Activity On Leaves Extract of Croton Sparsiflorious and Jatropha GossipifoliaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Activity of Acmella Paniculata Plant ExtractsDocument7 pagesPhytochemical and Antimicrobial Activity of Acmella Paniculata Plant ExtractsWinda AlzamoriNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Basing 2Document9 pagesJurnal Basing 2ikrimahNo ratings yet
- Article in Press: Isolation and Identification of An Antibacterial Compound From Diplotaxis Harra (Forssk.) BoissDocument7 pagesArticle in Press: Isolation and Identification of An Antibacterial Compound From Diplotaxis Harra (Forssk.) BoissIpah PahriahNo ratings yet
- ISSN No: 2456: International Open Access Journal International Open Access JournalDocument12 pagesISSN No: 2456: International Open Access Journal International Open Access JournalEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Effectiveness of Zingiber Officinale Plant Root Extract On Aspergillus Niger and Rhizopus Stolonifer Compared With Standard DrugDocument5 pagesAntifungal Effectiveness of Zingiber Officinale Plant Root Extract On Aspergillus Niger and Rhizopus Stolonifer Compared With Standard DrugInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Jotang 5Document4 pagesJotang 5Heriansyah S1 FarmasiNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activities of Medicinal PlantsDocument4 pagesAntimicrobial Activities of Medicinal PlantsarcherselevatorsNo ratings yet
- Screening of Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of Leaves ofDocument4 pagesScreening of Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities of Leaves ofTiên Đỗ Ngọc ThúyNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Activity of Alcoholic Leaf Extracts of TerminaliaDocument4 pagesAntifungal Activity of Alcoholic Leaf Extracts of TerminaliaAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Phytochemical Activities of Methanolic and Aqueous Extract of Cissus Aralioides Leaves On Some Selected Pathogenic MicroorganismsDocument5 pagesEvaluation of The Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Phytochemical Activities of Methanolic and Aqueous Extract of Cissus Aralioides Leaves On Some Selected Pathogenic MicroorganismsIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Sajp 42124 131Document8 pagesSajp 42124 131syamsu nurNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of The Antibacterial Activity of PiliostigmaDocument8 pagesA Comparative Study of The Antibacterial Activity of PiliostigmaglornumrNo ratings yet
- Research Plan 3Document8 pagesResearch Plan 3Grey GaleNo ratings yet
- Publikasi 2013jtpcDocument6 pagesPublikasi 2013jtpcputricetelNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2314808X17304530 MainDocument9 pages1 s2.0 S2314808X17304530 MainHagere EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Agar Well Diffusion MTDDocument7 pagesAgar Well Diffusion MTDRoland GealonNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activity of Azadirachita Indica and Psidium Guajava Extracts Against Three Bacterial Strains PDFDocument6 pagesAntibacterial Activity of Azadirachita Indica and Psidium Guajava Extracts Against Three Bacterial Strains PDFAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial, antifungal and anthelmintic activity of Morinda citrifoliaDocument3 pagesAntibacterial, antifungal and anthelmintic activity of Morinda citrifoliaVovi ApriliantiNo ratings yet
- HelenDocument4 pagesHelenAhmad BukhariNo ratings yet
- In Vitro & in Vivo Evaluations of Mikania Cordata (Bumr.f.) B.L. Robinson ExtractDocument9 pagesIn Vitro & in Vivo Evaluations of Mikania Cordata (Bumr.f.) B.L. Robinson Extractsomen mojumderNo ratings yet
- Fphar 09 00246 PDFDocument16 pagesFphar 09 00246 PDFDannyRomeroNo ratings yet
- A NidusDocument4 pagesA NidusJulio Francky Yannick TahinjanaharyNo ratings yet
- Comparative anthelmintic activity of Aegle marmelos Linn leaves and pulpDocument3 pagesComparative anthelmintic activity of Aegle marmelos Linn leaves and pulpSurya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activity of Medicinal Plant ExtractsDocument6 pagesAntimicrobial Activity of Medicinal Plant ExtractsMeiNo ratings yet
- Study Properties of Plant Medicated Green Synthesis of Silver NanoparticlesDocument4 pagesStudy Properties of Plant Medicated Green Synthesis of Silver NanoparticlesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Saponinas PDFDocument4 pagesSaponinas PDFJohnny Saavedra CamachoNo ratings yet
- 364 1401996255 PDFDocument5 pages364 1401996255 PDFraysellaNo ratings yet
- Comparatively Design and Analyze Elevated Rectangular Water Reservoir with and without Bracing for Different Stagging HeightDocument4 pagesComparatively Design and Analyze Elevated Rectangular Water Reservoir with and without Bracing for Different Stagging HeightInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3Document9 pagesDiabetic Retinopathy Stage Detection Using CNN and Inception V3International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera) Leaf Fiber as a Main Component in Making an Improvised Water FilterDocument11 pagesThe Utilization of Date Palm (Phoenix dactylifera) Leaf Fiber as a Main Component in Making an Improvised Water FilterInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Advancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning for Accurate Health Index PrognosisDocument8 pagesAdvancing Healthcare Predictions: Harnessing Machine Learning for Accurate Health Index PrognosisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)Document2 pagesDense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) in IT Networks: A Leap Beyond Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Electro-Optics Properties of Intact Cocoa Beans based on Near Infrared TechnologyDocument7 pagesElectro-Optics Properties of Intact Cocoa Beans based on Near Infrared TechnologyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Formulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Body ScrubDocument6 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Poly Herbal Body ScrubInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Terracing as an Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains- CameroonDocument14 pagesTerracing as an Old-Style Scheme of Soil Water Preservation in Djingliya-Mandara Mountains- CameroonInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Digital Marketing Dimensions on Customer SatisfactionDocument6 pagesThe Impact of Digital Marketing Dimensions on Customer SatisfactionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Review: Pink Eye Outbreak in IndiaDocument3 pagesA Review: Pink Eye Outbreak in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Auto Encoder Driven Hybrid Pipelines for Image Deblurring using NAFNETDocument6 pagesAuto Encoder Driven Hybrid Pipelines for Image Deblurring using NAFNETInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Design, Development and Evaluation of Methi-Shikakai Herbal ShampooDocument8 pagesDesign, Development and Evaluation of Methi-Shikakai Herbal ShampooInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (3)
- A Survey of the Plastic Waste used in Paving BlocksDocument4 pagesA Survey of the Plastic Waste used in Paving BlocksInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cyberbullying: Legal and Ethical Implications, Challenges and Opportunities for Policy DevelopmentDocument7 pagesCyberbullying: Legal and Ethical Implications, Challenges and Opportunities for Policy DevelopmentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Portovenous Gas in a Young MaleDocument2 pagesHepatic Portovenous Gas in a Young MaleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Explorning the Role of Machine Learning in Enhancing Cloud SecurityDocument5 pagesExplorning the Role of Machine Learning in Enhancing Cloud SecurityInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Navigating Digitalization: AHP Insights for SMEs' Strategic TransformationDocument11 pagesNavigating Digitalization: AHP Insights for SMEs' Strategic TransformationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Perceived Impact of Active Pedagogy in Medical Students' Learning at the Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy of CasablancaDocument5 pagesPerceived Impact of Active Pedagogy in Medical Students' Learning at the Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy of CasablancaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Automatic Power Factor ControllerDocument4 pagesAutomatic Power Factor ControllerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Distractions among Adolescents: Impact on Learning in the Aftermath of COVID-19 in IndiaDocument2 pagesMobile Distractions among Adolescents: Impact on Learning in the Aftermath of COVID-19 in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Review of Biomechanics in Footwear Design and Development: An Exploration of Key Concepts and InnovationsDocument5 pagesReview of Biomechanics in Footwear Design and Development: An Exploration of Key Concepts and InnovationsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Studying the Situation and Proposing Some Basic Solutions to Improve Psychological Harmony Between Managerial Staff and Students of Medical Universities in Hanoi AreaDocument5 pagesStudying the Situation and Proposing Some Basic Solutions to Improve Psychological Harmony Between Managerial Staff and Students of Medical Universities in Hanoi AreaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Time Variables as Predictors of Senior Secondary School Students' Mathematical Performance Department of Mathematics Education Freetown PolytechnicDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Time Variables as Predictors of Senior Secondary School Students' Mathematical Performance Department of Mathematics Education Freetown PolytechnicInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosage Control System Using Reinforcement LearningDocument8 pagesDrug Dosage Control System Using Reinforcement LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Securing Document Exchange with Blockchain Technology: A New Paradigm for Information SharingDocument4 pagesSecuring Document Exchange with Blockchain Technology: A New Paradigm for Information SharingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Enhancing the Strength of Concrete by Using Human Hairs as a FiberDocument3 pagesEnhancing the Strength of Concrete by Using Human Hairs as a FiberInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Formation of New Technology in Automated Highway System in Peripheral HighwayDocument6 pagesFormation of New Technology in Automated Highway System in Peripheral HighwayInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain 5.0: A Comprehensive Literature Review on Implications, Applications and ChallengesDocument11 pagesSupply Chain 5.0: A Comprehensive Literature Review on Implications, Applications and ChallengesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Engines: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Supply Chains with AIDocument14 pagesIntelligent Engines: Revolutionizing Manufacturing and Supply Chains with AIInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Making of Self-Disposing Contactless Motion-Activated Trash Bin Using Ultrasonic SensorsDocument7 pagesThe Making of Self-Disposing Contactless Motion-Activated Trash Bin Using Ultrasonic SensorsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- First Term QP - Paper 4 - 6 E-AssessmentDocument15 pagesFirst Term QP - Paper 4 - 6 E-Assessmentyossra_abdullaNo ratings yet
- Initial Efficacy and Tolerability of Early Enteral Nutrition With Immediate or Gradual Introduction in Intubated PatientsDocument6 pagesInitial Efficacy and Tolerability of Early Enteral Nutrition With Immediate or Gradual Introduction in Intubated PatientsUCI COVID Pediátrico HNGAINo ratings yet
- Safety Seal Certification Checklist: (DILG As Issuing Officer)Document3 pagesSafety Seal Certification Checklist: (DILG As Issuing Officer)bash bashNo ratings yet
- Dr. Diksha Rajput PG Activity FinalDocument8 pagesDr. Diksha Rajput PG Activity FinalHamzah AsifNo ratings yet
- HTTPS://WWW - Scribd.com/document/516867318/araling Panlipunan 10 Module 1 1st Quarter 1Document2 pagesHTTPS://WWW - Scribd.com/document/516867318/araling Panlipunan 10 Module 1 1st Quarter 1Aleckz MinaNo ratings yet
- Asal PBF ObatDocument212 pagesAsal PBF ObatKlinik Pratama LarisaNo ratings yet
- E Brosur NMW Clinic 20211Document27 pagesE Brosur NMW Clinic 20211nirmalazintaNo ratings yet
- Form-1-3-MR-TdHPV-Masterlisting-Form-1 HESTIADocument3 pagesForm-1-3-MR-TdHPV-Masterlisting-Form-1 HESTIAMay John Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Hofstra Religious Vaccine ExemptionDocument2 pagesHofstra Religious Vaccine ExemptionThe Blackstone ProjectNo ratings yet
- Dräger Oxylog 3000 Plus Emergency & Transport VentilationDocument8 pagesDräger Oxylog 3000 Plus Emergency & Transport VentilationHAITHM MURSHEDNo ratings yet
- Aarogya Courses List PDFDocument9 pagesAarogya Courses List PDFankitsinghchauhanNo ratings yet
- Hardani Prisma Rizky, Wara Pramesti, and Gangga AnuragaDocument15 pagesHardani Prisma Rizky, Wara Pramesti, and Gangga AnuragaUp ToyouNo ratings yet
- Session PlanDocument9 pagesSession PlanKirsten Q. CaminongNo ratings yet
- DHHS Letter To Rep. Kathy ManningDocument4 pagesDHHS Letter To Rep. Kathy ManningSteven DoyleNo ratings yet
- Multi Bandage Presentation - URIEL Meditex LTDDocument9 pagesMulti Bandage Presentation - URIEL Meditex LTDIsrael ExporterNo ratings yet
- Edited Proposal.4TZ-Nsg ProcessDocument49 pagesEdited Proposal.4TZ-Nsg ProcessDawit DesalegnNo ratings yet
- 1 Making Occlusion - TerminologyDocument7 pages1 Making Occlusion - TerminologyAli QawasNo ratings yet
- AHDP - Teenage Pregnancy NewDocument20 pagesAHDP - Teenage Pregnancy NewEdisa AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Mindray PM 8000 Express User ID10229Document324 pagesMindray PM 8000 Express User ID10229Salmon 123No ratings yet
- Stock 15 Mar 21Document14 pagesStock 15 Mar 21Esha April MaharaniNo ratings yet
- JKT Surveillance PPRA 2021Document28 pagesJKT Surveillance PPRA 2021priyantoNo ratings yet
- Tablet Manufacturing ProcessDocument8 pagesTablet Manufacturing ProcessNaveen KingNo ratings yet
- ToxicologyDocument10 pagesToxicologyRohith TejaNo ratings yet
- Boq Medical Services Obs™ PDFDocument3 pagesBoq Medical Services Obs™ PDFKyle Levic SalaguintoNo ratings yet
- Declaration FormDocument1 pageDeclaration FormHAIZA FATHIMA100% (1)
- Man Held in Theft Case Dies in Police Custody in ThanjavurDocument8 pagesMan Held in Theft Case Dies in Police Custody in ThanjavurSureshkumar JNo ratings yet